 Gaseous carbon dioxide (CO2) can be captured using aqueous organic amines such as ethanolamine prior to storage, reuse, or sequestration. The reversible amine-based absorption−desorption capture process is regarded as the most mature and economical technology due to its extensive use in related industrial applications.
Gaseous carbon dioxide (CO2) can be captured using aqueous organic amines such as ethanolamine prior to storage, reuse, or sequestration. The reversible amine-based absorption−desorption capture process is regarded as the most mature and economical technology due to its extensive use in related industrial applications.
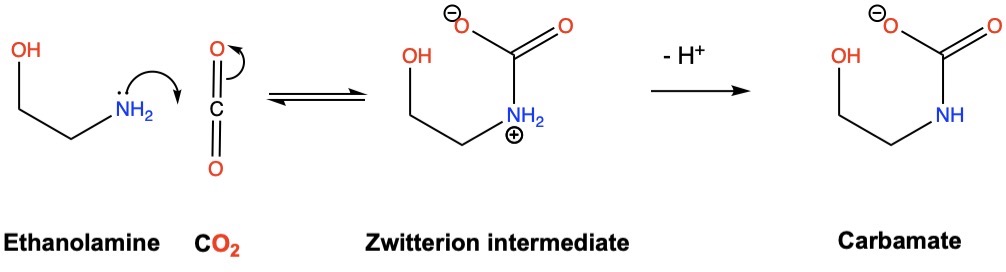
Nucleophilic attack of the primary amine on carbon dioxide produces a zwitterion intermediate containing an ammonium cation and a carboxylate anion. The ammonium cation can then lose a proton to a base to form the carbamate anion.
Click the buttons or use the Controls tab to view the 3D animation of the addition of the amine to CO2