Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
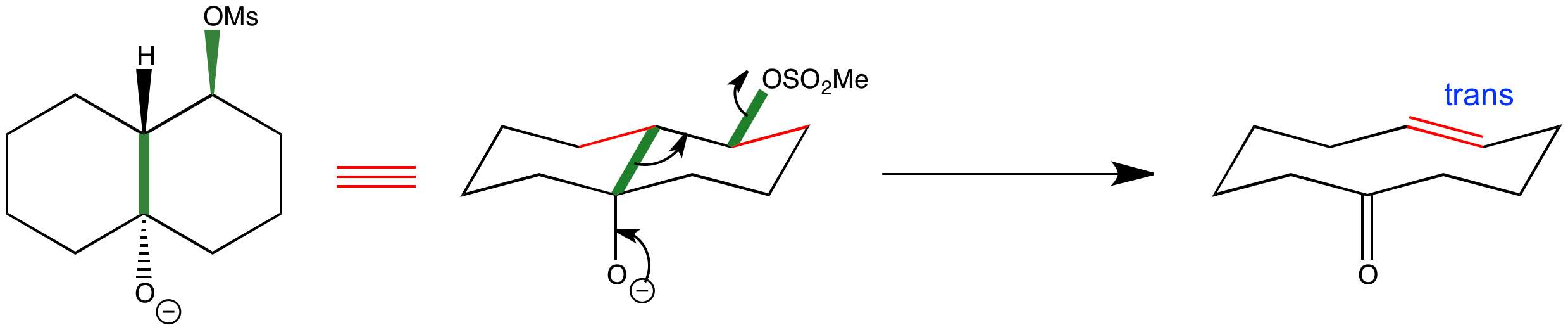
This diastereoisomer undergoes ring expansion to form a ten-membered ring with a trans double bond. Looking at the alignment of the bonds that end up flanking the double bond (red bonds) shows you where the geometrical isomer comes from. The fragmentation reaction occurs because the breaking carbon-carbon bond and the leaving group (green bonds) are anti-periplanar to one another.
Back to diastereoisomer main page
M. A. Drahl, M. Manpadi and L. J. Williams, Angew. Chemie – Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 11222–11251.