Click the reaction arrow in the sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
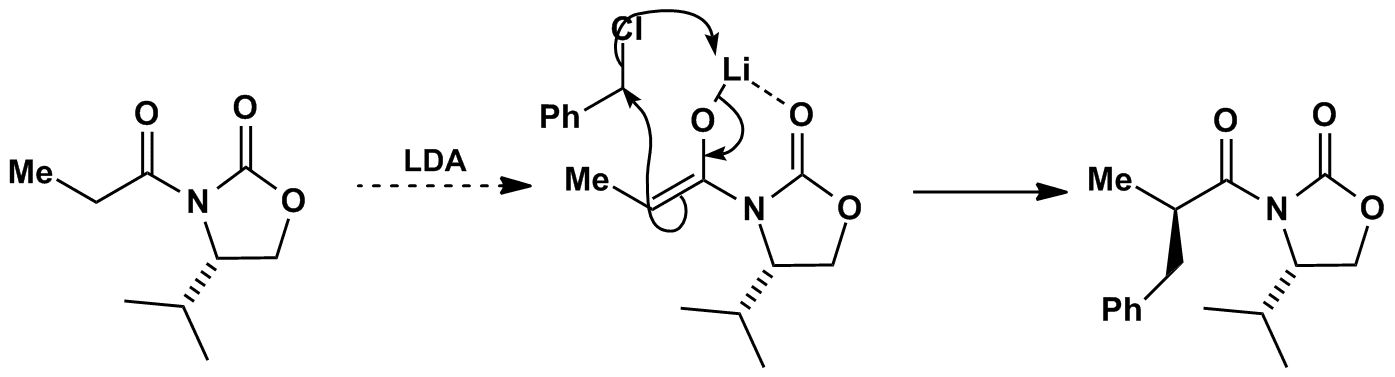
Deprotonation with LDA produces the Z-enolate. Chelation of the auxiliary carbonyl to the lithium restricts the conformation so that the isopropyl group shields the bottom face of the enolate. Electrophiles react on the less hindered top face with high diastereoselectivity. Removal of the auxiliary gives enantiomerically enriched alpha-alkylated acid derivatives.
D. A. Evans, M. D. Ennis and D. J. Mathre, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1982, 104, 1737–1739.