Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
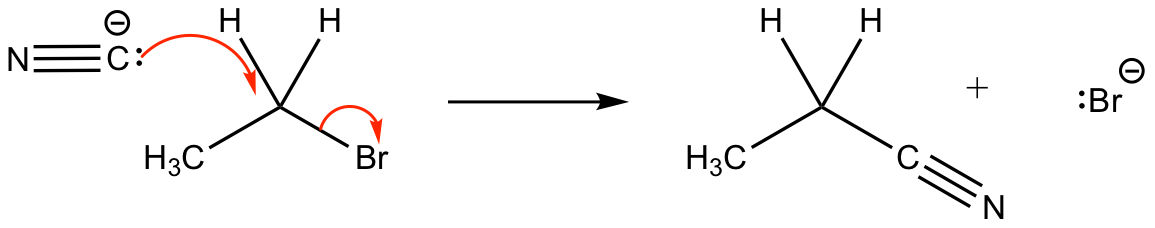
This is a nucleophilic substitution mechanism of a cyanide (CN–) ion. This mechanism occurs when potassium cyanide (KCN) is added to a warmed haloalkane (in this case ethyl bromide, though any haloalkane can be used).
Halogen atoms are electronegative so C-X bonds are polar, with the electrons being attracted by the halogen (which becomes slightly negative). The slight positive charge on the carbon makes it susceptible to attack by a nucleophile (electron pair donor). The reaction results in the C-X bond breaking and the nucleophile taking the place of the halogen.