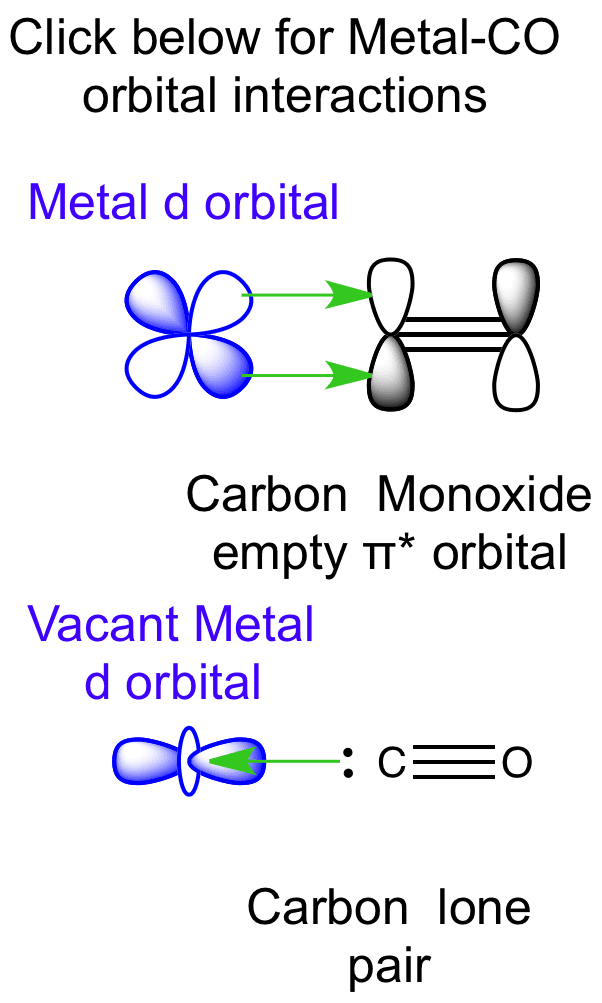
When acting as a ligand to a metal centre, carbon monoxide is capable of forming a metal-carbon σ bond via donation of a lone pair from carbon. It can also accept π-electron density from filled d-metal orbitals into the CO π antibonding orbital. Hence CO can be considered a Lewis σ base and a Lewis π acid, which is capable of stabilising low oxidation state metals. This type of π bonding is referred to as π backbonding.
Explore Metal-Ligand bonding with other molecules
Carbon Monoxide | Phosphine | Hydrogen | Ethylene | Cyclobutadiene | Butadiene | Benzene | Allyl | Cyclopentadienyl | Carbene