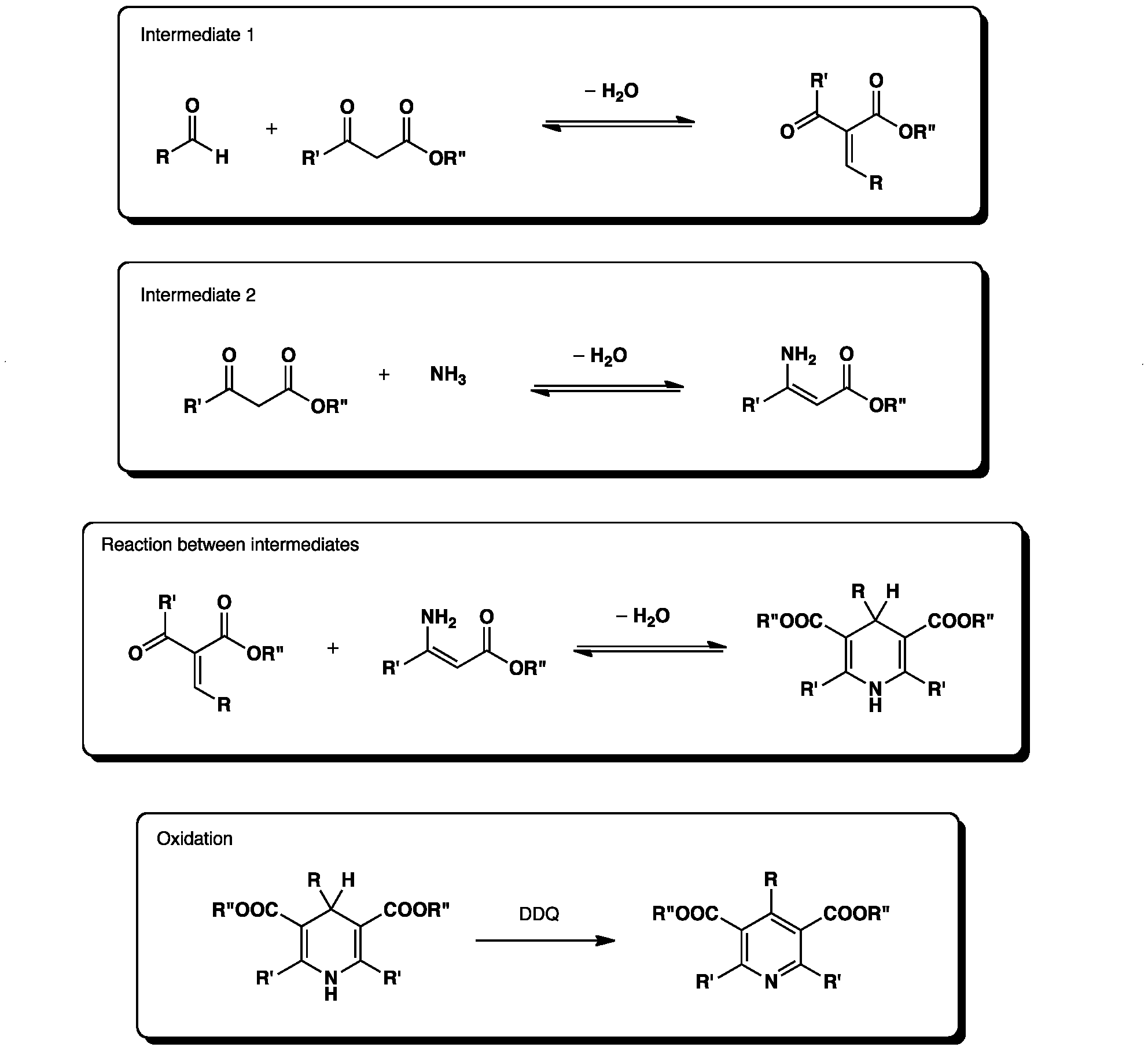
The Hantzsch synthesis is a four-component reaction between an aldehyde, two equivalents of a β-ketoester and ammonia, followed by oxidation to give a pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate. Subsequent decarboxylation gives the corresponding pyridines.
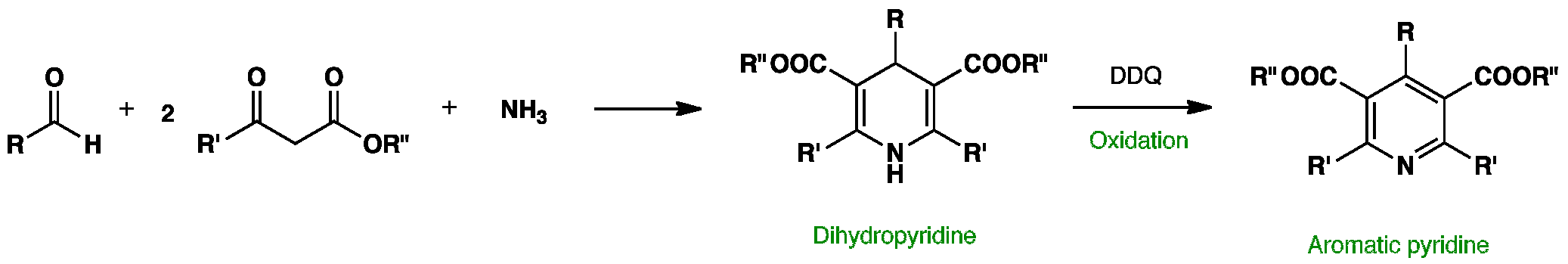
Click the different stages to view the 3D models of the reaction:
H. G. O. Alvim, E. N. da Silva Júnior and B. A. D. Neto, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 54282–54299.