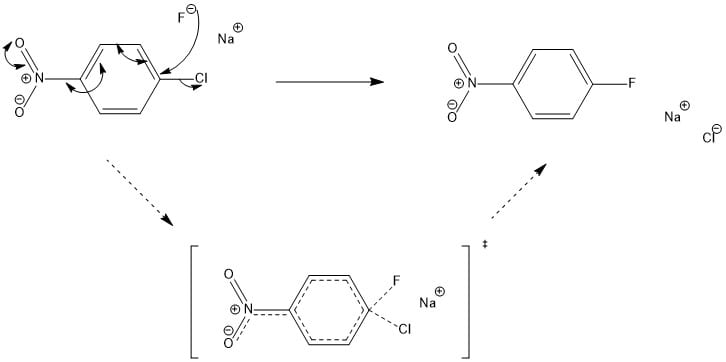
Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
The Halex reaction (shown above) is one possible reaction to synthesize fluorinated compounds from chlorinated compounds. The mechanistic pathway is a nucleophilic aromatic exchange of halogens (SNAr). The Halex reaction is usually carried out using polar aprotic solvents (DMSO) and using a nucleophilic source of fluorine (KF, NaF, CsF, etc) at a temperature below the boiling point of the solvent used. The reaction itself is operated under reflux for 1.5 to 2 hours and the fluorinated compounds can be produced in synthetically useful yields of 80-90%. Another possible way of producing fluorinated drug compounds is by electrophilic substitution using N-Fluoro reagents.