Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
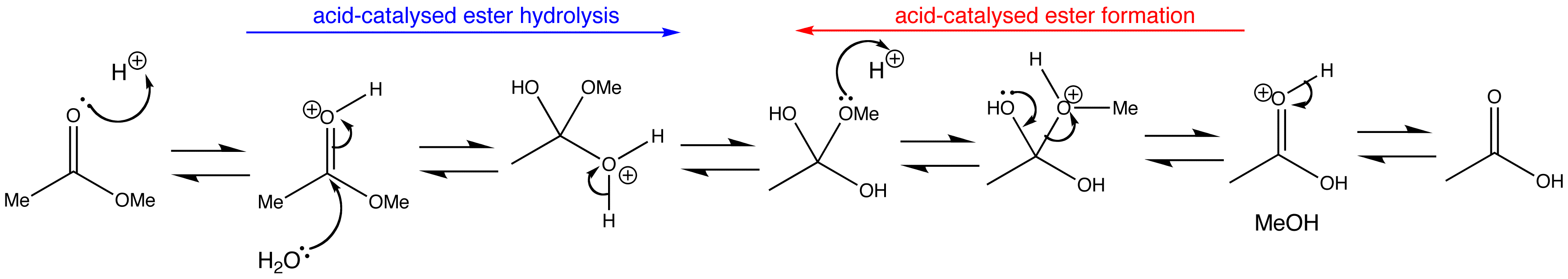
Acid-catalysed ester formation and hydrolysis are the exact reverse of one another. The only way to control the reaction is by altering the concentrations of the reagents to drive the reaction the way we want it to go. An excess of water forces the hydrolysis of the ester, whereas an excess of ester or removal of water forces the reverse reaction, that is the formation of ester.
E. Haslam, Tetrahedron, 1980, 36, 2409–2433.