Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
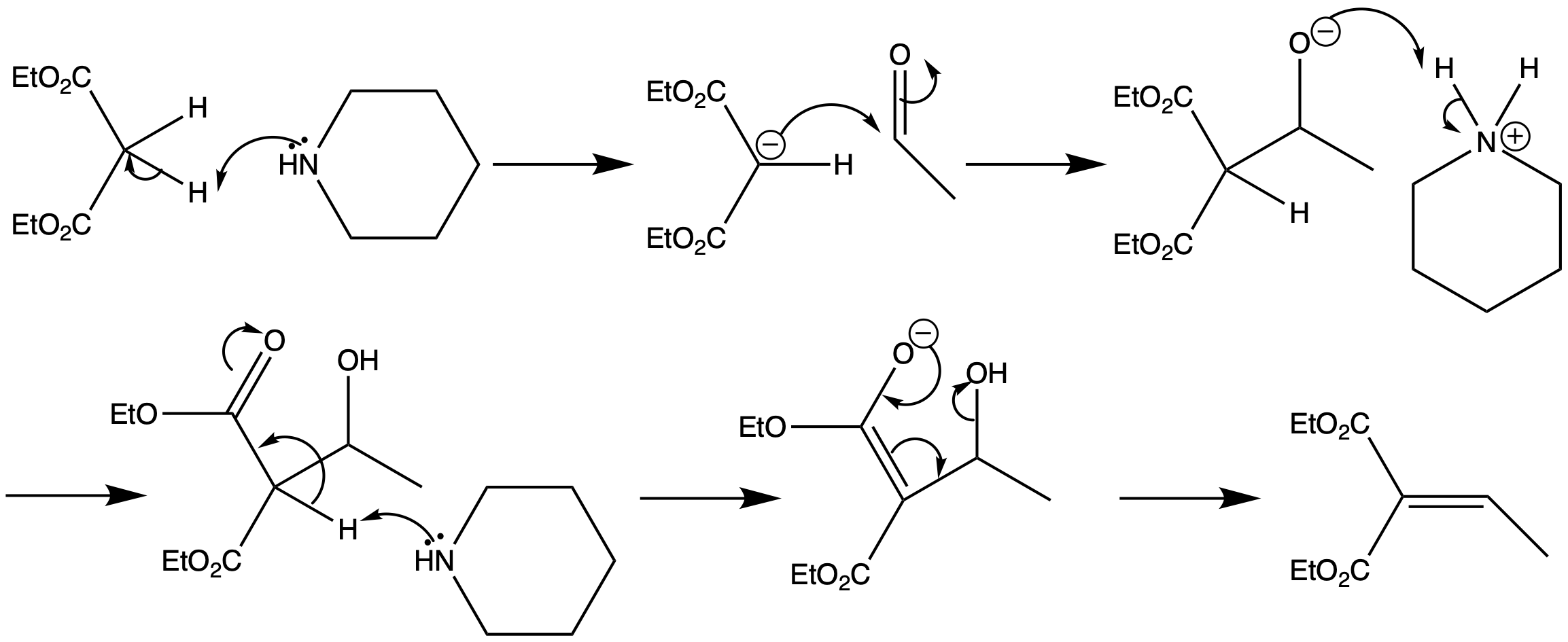
The Knoevenagel condensation is the reaction of stabilised carbanions with carbonyl compounds. A secondary amine is used as the base, as it allows partial deprotonation of a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound but not of a normal aldehyde, so self-condensation of the aldehyde is not a problem.
E. V. Dalessandro, H. P. Collin, M. S. Valle and J. R. Pliego, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 57803–57810.