Click the structures to view the separate chain reaction steps in more detail
Chloroalkanes are alkanes with one or more hydrogen atoms substituted by a chlorine atom.
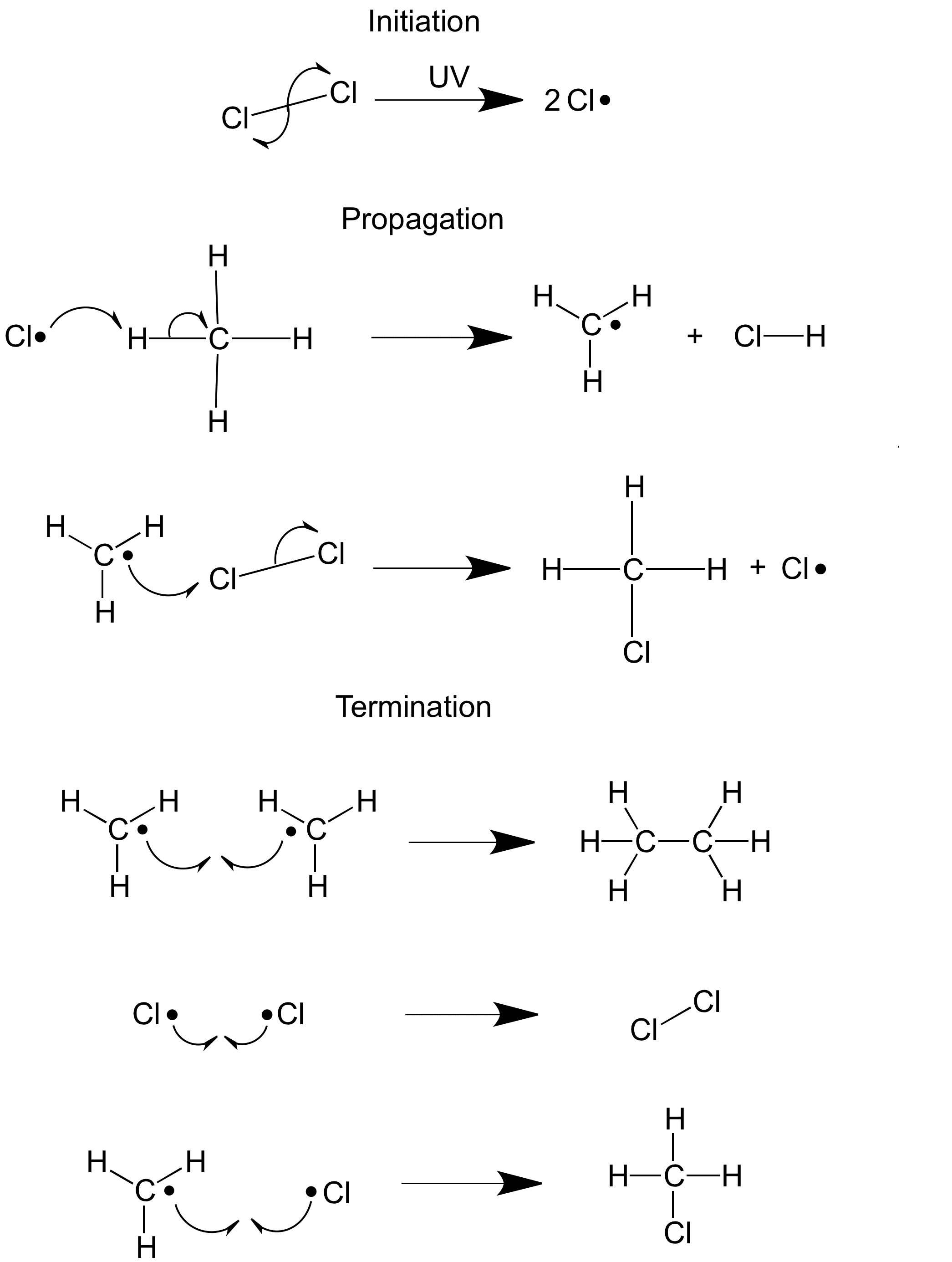
Halogens react with alkanes in photochemical reactions to form haloalkanes. Photochemical reactions are started by ultraviolet light. A hydrogen atom is substituted by chlorine. This is a free radical substitution reaction.
Free radicals are molecules with an unpaired electron, written like Cl• or CH3•. Free radicals are highly reactive and the result of bonds splitting equally – initiation reaction.
The reaction mechanism for the synthesis of chlormethane is shown above and happens when a mixture of methane and chlorineare exposed to UV light. The overall equation is: CH4 + Cl2 -> CH3Cl + HCl
The reaction mechanism shows each step in the synthesis, in this case the free radical chain reaction has three stages – initiation, propagation and termination.
These pages have been made to incorporate different UK Chemistry A Level specifications.
To see your specific specification choose from below: