Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
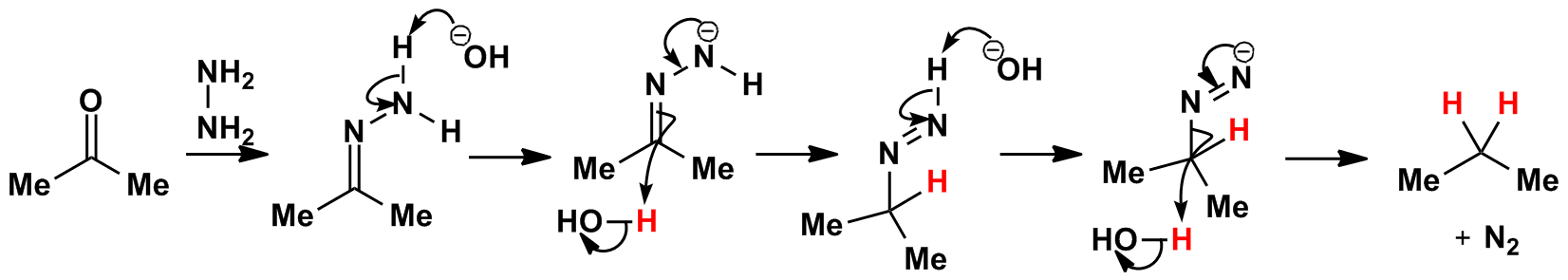
The ketone is first converted to a hydrazone via the hydrazine (H2NNH2) reagent. Click here to view this mechanism. This then undergoes reduction by hot concentrated sodium hydroxide. The reaction works due to the thermodynamic stability of N2.