Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
View the stereochemical properties of these reactions
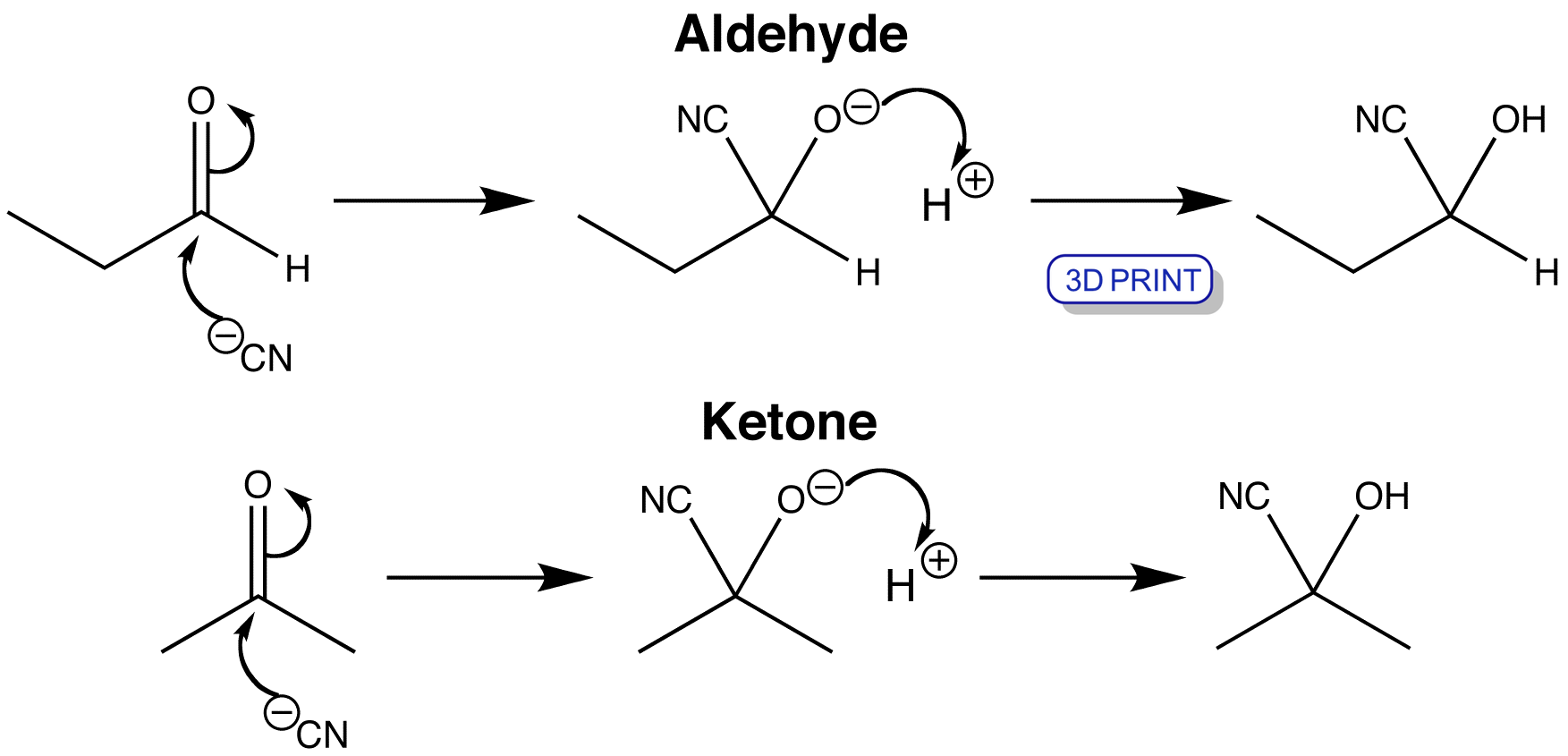
Cyanohydrin formation can occur via the attack of cyanide to both aldehydes and ketones, usually in the presence of acid which protonates the resulting alkoxide to give the hydroxy group. Cyanide contains sp hybridised C and N atoms, and its HOMO is an sp orbital on carbon. The reaction is a typical nucleophilic addition reaction to a carbonyl group, with the electron pair from the HOMO of the cyanide (an sp orbital on carbon) moving into the C=O π* orbital, and the electrons from the C=O π orbital moving onto the oxygen atom.
M. North, Synlett, 1993, 1993, 807–820.