Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
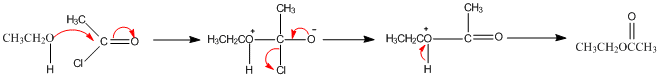
Ethyl ethanoate is synthesised in a three step process as shown above. First, there is an initial nucleophilic addition of an alcohol to the carbonyl group, this then undergoes an elimination reaction before finally reaching the product.
Ethyl ethanoate is commonly known as ethyl acetate. It is used as a solvent within a laboratory situation. In other industries, it is used to decaffinated coffee and is used as a preserving agent in entomology.