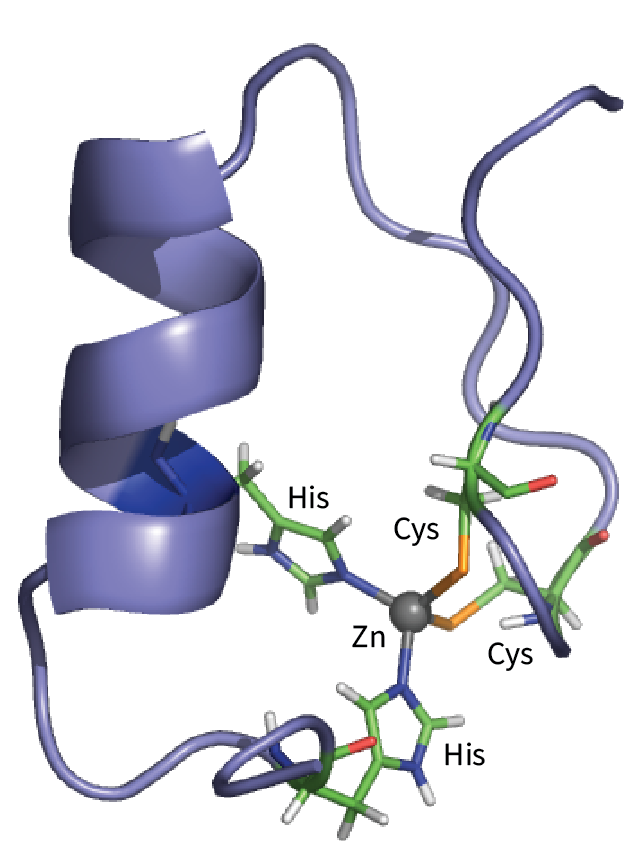
Zinc fingers are protein folds that expose and project a series of amino acids able to recognize and interact with specific base sequences on DNA. A typical finger is formed by the coordination of Zn(II) to two pairs of amino acid side chains located either side of the ‘fingertip’.