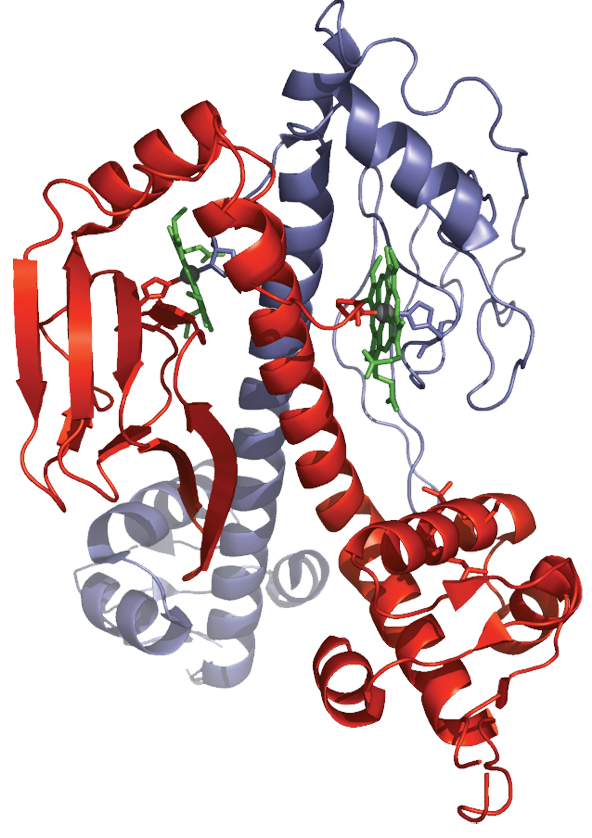
The structure of CooA, a bacterial CO sensor and transcription factor. The molecule, a dimer of two identical subunits (represented as red and blue) has two haem binding domains and two ‘helix–turn–helix’ domains that recognize a section of DNA. The protein ligands to the Fe atoms are a histidine from one subunit and an N-terminal proline from the other. The binding of CO and displacement of proline disrupts the assembly and allows CooA to bind to DNA.