Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
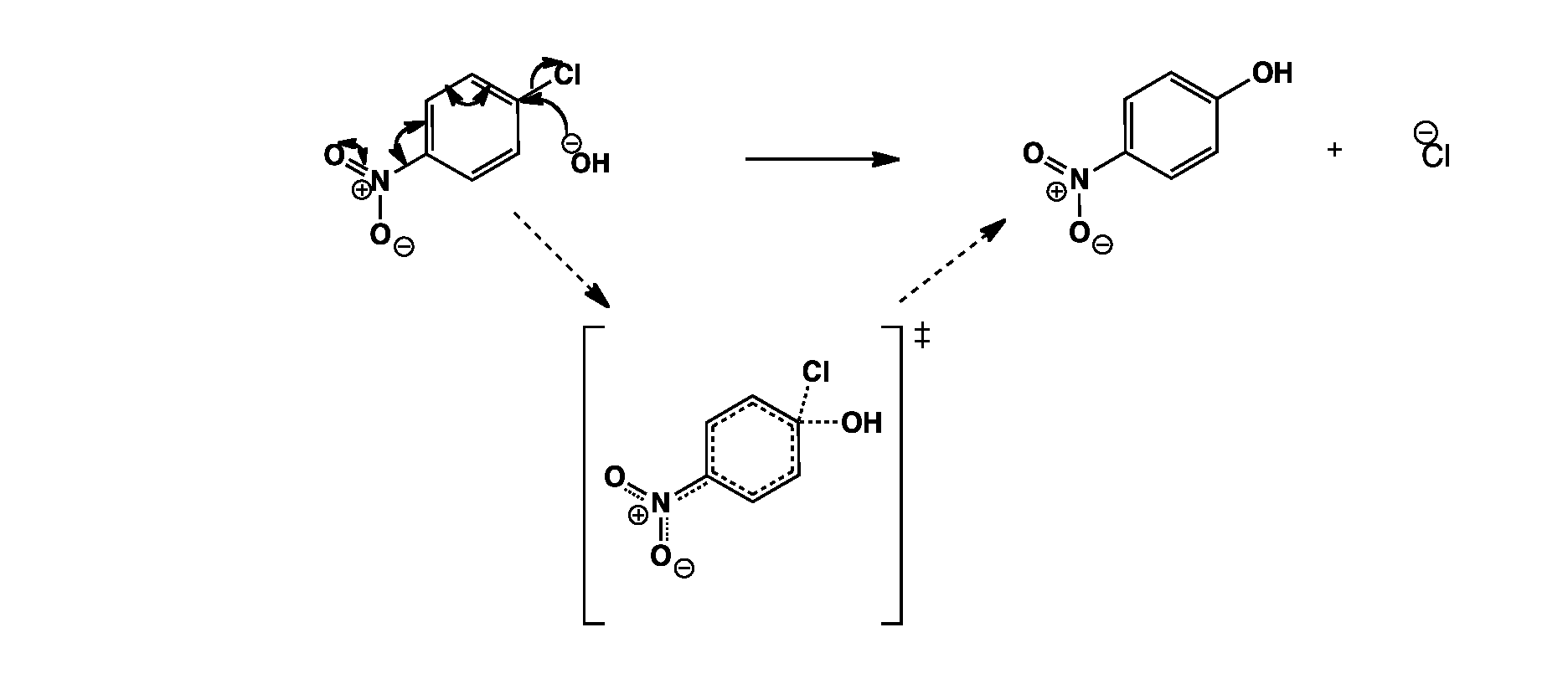
The hydroxide anion attacks para to the nitro group. The negative charge is delocalised around the ring to the nitro group which helps stabilise the transition state. The chloride anion is then eliminated.
Related Halex reaction and alternative benzyne intermediate mechanism.