Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
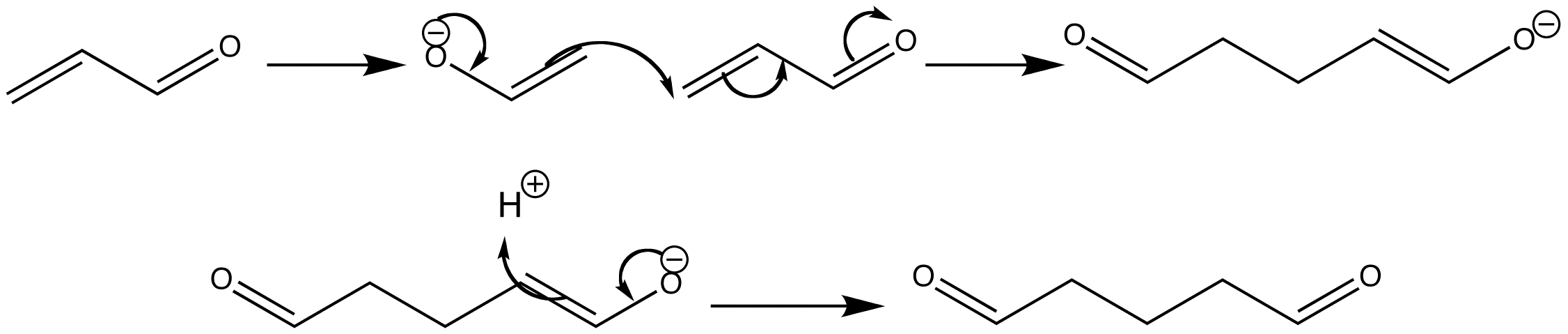
The enolate carbon attacks the conjugated system of the enone to form a new enolate. This reaction is known as conjugate addition because it requires a conjugated system. Protonation reforms the carbonyl group.
Back to Conjugate addition summary
A. G. Csákÿ, G. de la Herrán and M. C. Murcia, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 4080.