Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
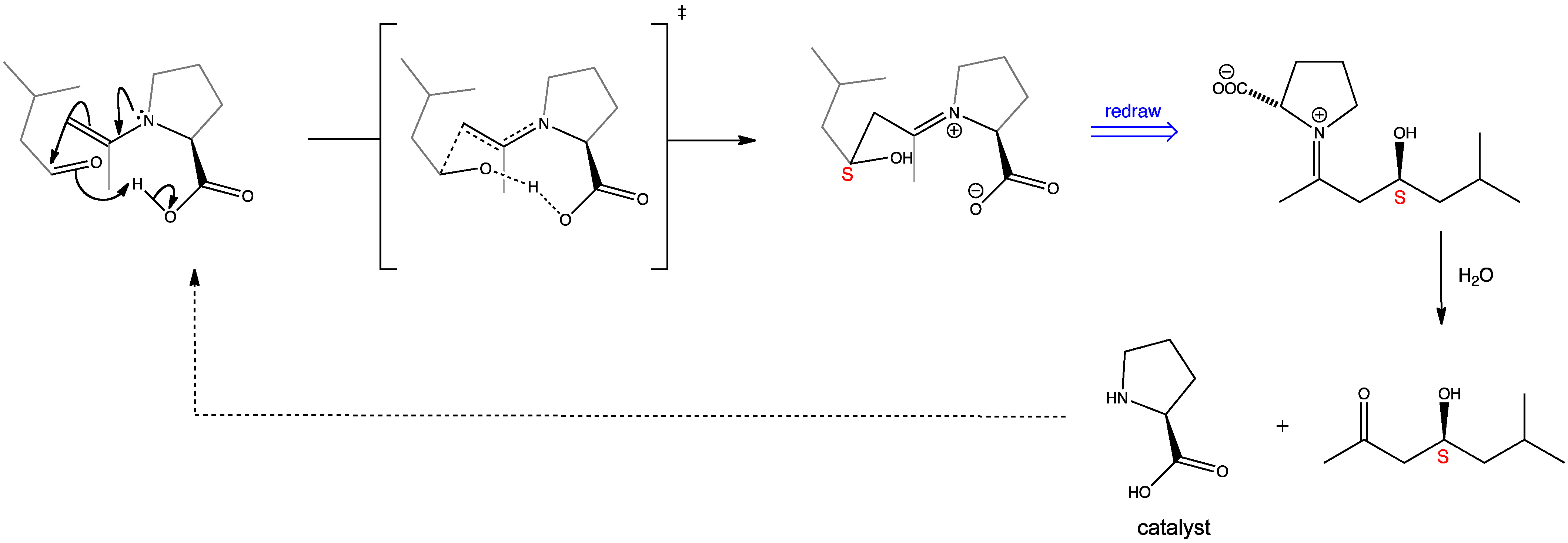
The initial interaction between proline and acetone generates an enamine intermediate, which then reacts further with an aldehyde to yield the aldol product. The reaction is controlled by a hydrogen-bonded transition state in which the aldehyde substituent occupies an equatorial position on the chair-like structure. The product is obtained in high enantioselectivity due to the proline catalyst.