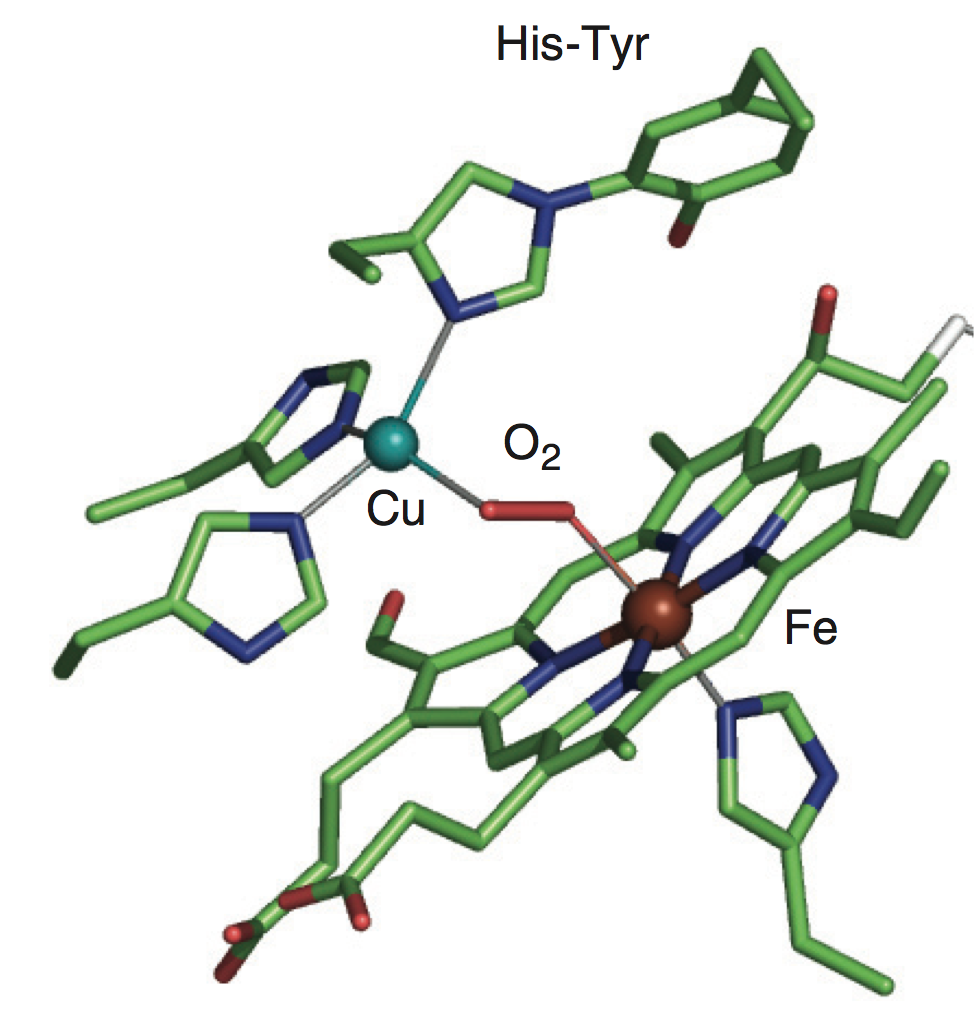
The structure of cytochrome C oxidase as it occurs in the membrane, showing the locations of the redox centres and the sites for reaction with O2 and cytochrome C.
Cytochrome C oxidase is a membrane-bound enzyme that catalyses the four-electron reduction of O2 to water, using cytochrome C as the electron donor. The active site for O2 reduction consists of a myoglobin-like Fe–porphyrin (haem-a3) that is adjacent to a ‘semi-haemocyanin-like’ Cu (known as CuB) coordinated by three histidine ligands