Step 3 – Acid catalysed dehydration
Click the structures and reaction arrows in sequence to view the 3D models and animations respectively
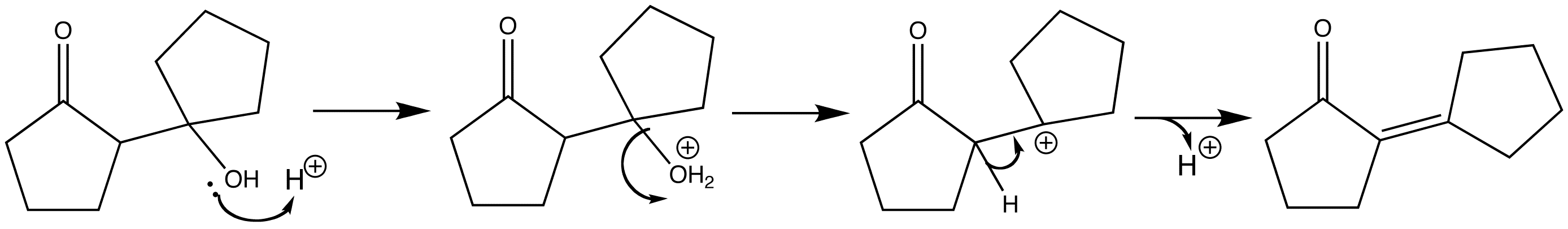
The aldol product can then undergo an acid-catalysed dehydration step via an E1 mechanism. The carbonyl group ensures that only the stable conjugated enone is formed. Firstly the alcohol groups of the aldol is protonated, and then the water acts as a leaving group to give the carbon a positive charge. A proton is then lost from the adjacent carbon to form the C=C double bond.
<Back to cyclopentanone aldol summary
D. S. Noyce and W. A. Pryor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1955, 77, 1397–1401.
C. L. Perrin and K.-L. Chang, J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 5631–5635.